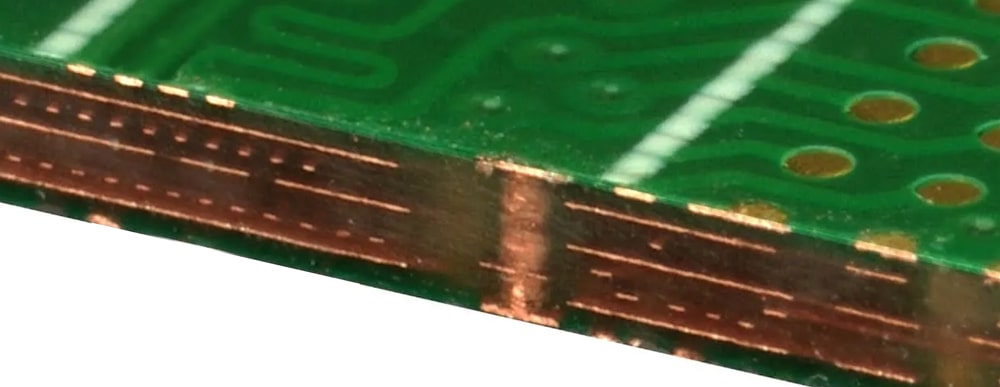
Is thickness important for a PCB?
12 December 2025
Views: 541
PCB thickness is a critical parameter in circuit board design and manufacturing. Different thicknesses are used for different purposes. So does thickness matter for PCBs?
Standard Thickness
The most common PCB thickness is 1.6 mm (0.062 inches), which is often used in consumer electronics. However, depending on specific needs, PCB thickness can range from 0.4 mm to 3.2 mm. Each standard thickness has its typical applications and advantages.
0.4 mm - 0.6 mm Thickness
Ultra-thin PCBs are mainly used in mobile devices, wearable devices, and compact electronics, with excellent flexibility and space efficiency, but require careful handling during assembly and have limited number of layers.
1.0 mm Thickness
This thickness is common in automotive electronics and industrial control systems, and strikes a balance between durability and space while maintaining sufficient rigidity for most applications.
1.6 mm Thickness
Industry standard thickness provides the best mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, is suitable for most general applications, and can accommodate a wide range of layer counts.
2.0mm - 3.2mm Thickness
Thicker PCBs are often used in high-power applications, military equipment, and where superior mechanical strength is required, have better heat dissipation, and can withstand higher current loads.
PCB thickness affects several key factors: 1. Signal integrity; 2. Heat dissipation; 3. Mechanical stability; 4. Component compatibility. We will not go into this here.
Conclusion
The choice of PCB thickness depends on a variety of factors, including application requirements, component selection, environmental conditions, and cost constraints. It is important for engineers to carefully balance these factors and select the optimal thickness for a specific application.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!

 Email: all@poe-pcba.com
Email: all@poe-pcba.com
 Whatsapp: 85292069596
Whatsapp: 85292069596
 Tel: 0755-25312250/ +8613798543496
Tel: 0755-25312250/ +8613798543496
 Factory Address: Floor 3, Jinyuan Industrial Park, No. 56, Tangtou Avenue, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen China
Factory Address: Floor 3, Jinyuan Industrial Park, No. 56, Tangtou Avenue, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen China